W02 Learning Activity: Handling DOM Events
Overview
Handling DOM events in JavaScript is a fundamental part of building interactive web pages. In this activity, you'll learn about the different events you can handle, how to handle them, and how to pass data between the event handler and the rest of your code.
"Events are things that happen in the system you are programming—the system produces (or "fires") a signal of some kind when an event occurs, and provides a mechanism by which an action can be automatically taken (that is, some code running) when the event occurs. Events are fired inside the browser window and tend to be attached to a specific item that resides in it." – MDN
Prepare
- Reference: Introduction to Events – MDN
- Practice: Common DOM event concepts and use cases. These are just a few examples; there
are many other events and use cases.
- Click Event: Triggered when a user clicks on an element. It's widely used for handling
button clicks, link clicks, or any interaction involving a mouse click.
buttonElement.addEventListener('click', function() { // Code to execute when the element is clicked });The
addEventListenermethod takes two arguments: the event name and a function to execute when the event is triggered. This function is called an event handler. We will learn more about writing functions later in the course. For now, just know that the function is a block of code that will execute when the event is triggered. The function is also called a callback function because it is "called back" when the event is triggered. - Keyup Event: Triggered when a key is released. Useful for
handling keyboard input.
buttonElement.addEventListener('keyup', function() { // Code to execute when a key is released }); - DOMContentLoaded Event: Triggered when the HTML document has been
completely parsed and all deferred scripts have been executed. It's widely used for
initializing JavaScript applications.
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() { // Code to execute when the DOM is parsed });
- Click Event: Triggered when a user clicks on an element. It's widely used for handling
button clicks, link clicks, or any interaction involving a mouse click.
Activity Instructions
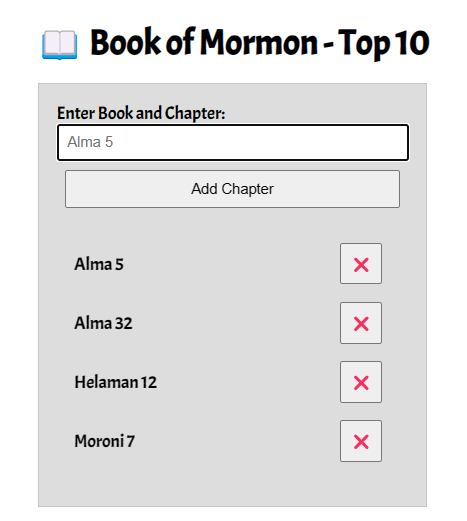
This activity adds functionality to the BOM Top 10 application started in the previous learning activity on DOM manipulation. We will organize the code to respond to the Add Chapter button click to build the list item. In addition, delete button functionality will be added along with some user interface improvements.
- Open your JavaScript file that is supporting the bom.html application, if needed.
- Create a click event listener for the Add Chapter button
with
addEventListener.
Check Your Understanding
button.addEventListener('click', function() { // Code to execute when the button is clicked }); - Within the Add Chapter button click event function block (between the
opening and closing braces of the callback function { ... }), complete the following tasks:
- Check to make sure the input is not blank before completing the remaining tasks in this list. Use an
ifblock that either provides a message or does nothing and returns the.focus()to the input field.Check Your Understanding
if (input.value.trim() !== '') { ... }What does the .trim() method do?
Should an else branch be added to this conditional?
What code should go into the condition true block { ... }? - Move the code that you wrote in the last activity into this
ifblock to support the correct flow of the program.Check Your Understanding
When the user clicks the Add Chapter button, the program checks to make sure that the input field is not empty. If the input is valid, the program creates and populates the list elements. - Add an event listener to the delete button that removes the li element when clicked.
Check Your Understanding
deleteButton.addEventListener('click', function () { list.removeChild(li); input.focus(); });This event listener demonstrates Event Delegation, which is an efficient way to handle events on multiple elements (the BOM chapters). Instead of adding an event listener to each individual delete button, you add a single event listener to each delete button as it is created. This approach is especially useful when elements are dynamically added to the DOM.
- Change the input value to an empty string to clean up the interface for
the user.
Check Your Understanding
input.value = ''; - After processing, the focus (active cursor) should be sent to the input element.
Check Your Understanding
input.focus();
- Check to make sure the input is not blank before completing the remaining tasks in this list. Use an
Example Solution
CodePen ⚙️ BOM Top 10
Testing & Submission
- Thoroughly test your application in the browser. This can be done locally.
- What else would you add to increase this application's usability?
Ideas to consider
- Validate input — Only accept Book of Mormon books
- Limit to 10 entries — Enforce the "Top 10" constraint
- Prevent duplicates — Don't allow the same chapter to be added more than once
- Better UI feedback — Show warnings/confirmations
- Improve accessibility — Ensure the application is usable with screen readers and keyboard navigation
- Format input — Standardize the format of the input for consistency
- Commit and push your work to your GitHub Pages enabled wdd131 repository.
