W03 Project: Water Pressure
Purpose
Prove that you can write and run test functions to help you find and fix mistakes in a Python program.
Project
Do not use AI to generate the code for this program.
Using AI to generate this program is a violation of the course AI policy and may result in receiving a 0 on the assignment, failing the course, or being removed from the program.
If you need help on the assignment or have questions about AI use, please ask your instructor.
Your town needs a volunteer to finish writing and testing a computer program that will be used to help design a new drinking water system.
Background
The small town you live in has received a grant to build and install a freshwater supply system for your community. This will bring great benefit to your community, providing clean water for all. The grant will cover the cost of materials but not the labor to do the job. The city has assembled volunteers to help design and install this new water system.
The team has decided to build an elevated water tank and install a pump that pushes water up to the tank where the water is stored. When a person opens a water faucet, water runs from the tank through pipes to the faucet. Earth’s gravity pulling on the water in the elevated tank pressurizes the water and causes it to flow from the faucet.
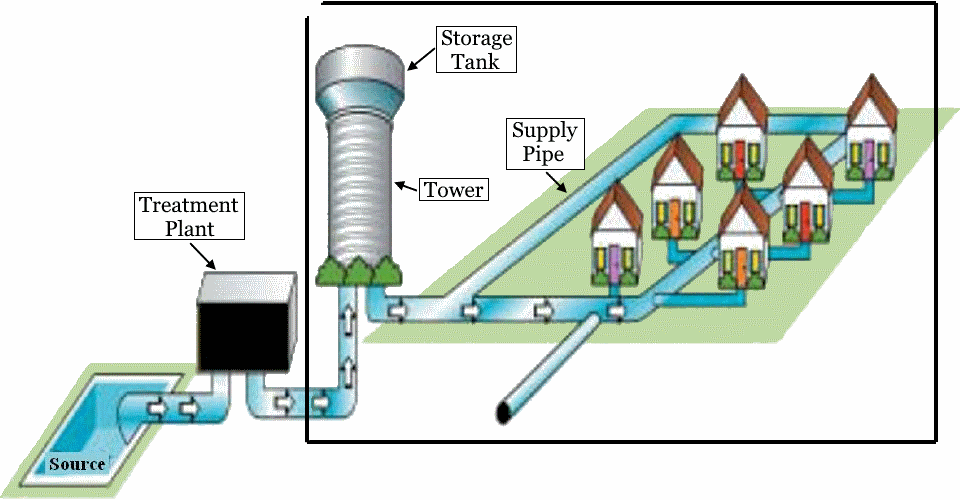
The team must design the system and ensure water will flow to all buildings. To accomplish this the designer must choose the tower height, pipe type, pipe diameter, and pipe path.
A computer program was written by a volunteer to help with the design, but when the team started to use the program, the numbers didn't seem to be correct. The original programmer is not available to fix the program so you have been asked to help out. Your task is to find out why the program is not working correctly, fix it, and prove that you fixed it. To do this you will need to write unit tests to prove the functions operate according to specifications.
Requirements
The following functions need to be fixed and validated.
-
Water Column Height
def water_column_height(tower_height, tank_height):
h = t +3w4Formula details:
Use the following formula details to calculate the function's return value.
-
h is height of the water column
-
t is the height of the tower (
tower_height) -
w is the height of the walls of the tank that is on top of the tower (
tank_height)
-
-
Pressure gain from height
def pressure_gain_from_water_height(height):
P =ρgh1000Formula details:
Use the following formula details to calculate the function's return value.
-
P is the pressure in kilopascals
-
ρ is the density of water 998.2 (kilogram / meter3)
-
g is the acceleration from Earths gravity 9.80665 (meter / second2)
-
h is the height of the water column inmeters (
height)
-
-
def pressure_loss_from_pipe(pipe_diameter, pipe_length, friction_factor, fluid_velocity):
P =− f L ρ v22000 dFormula details:
Use the following formula details to calculate the function's return value.
-
P is the lost pressure in kilopascals
-
f is the pipe’s friction factor (
friction_factor) -
L is the length of the pipe in meters (
pipe_length) -
ρ is the density of water 998.2 (kilogram / meter3)
-
v is the velocity of the water flowing through the pipe in meters / second (
fluid_velocity) -
d is the diameter of the pipe in meters (
pipe_diameter)
-
-
Pressure loss from fittings
def pressure_loss_from_fittings(fluid_velocity, quantity_fittings):
P =−0.04 ρ v2 n2000Formula details:
Use the following formula details to calculate the function's return value.
-
P is the lost pressure in kilopascals
-
ρ is the density of water (998.2 kilogram / meter3)
-
v is the velocity of the water flowing through the pipe in meters / second (
fluid_velocity) -
n is the quantity of fittings (
quantity_fittings)
-
-
Reynolds Number
def reynolds_number(hydraulic_diameter, fluid_velocity):
R =ρdvμFormula details:
Use the following formula details to calculate the function's return value.
-
R is the Reynolds number
-
ρ is the density of water (998.2 kilogram / meter3)
-
d is the hydraulic diameter of a pipe in meters. For a round pipe, the hydraulic diameter is the same as the pipe’s inner diameter. (
hydraulic_diameter) -
v is the velocity of the water flowing through the pipe in meters / second (
fluid_velocity) -
μ is the dynamic viscosity of water (0.0010016 Pascal seconds)
-
-
Pressure loss from pipe reduction
def pressure_loss_from_pipe_reduction(larger_diameter, fluid_velocity, reynolds_number, smaller_diameter):
k =0.1 +50R4 − 1DdP =− k ρ v22000Formula details:
Use the following formula details to calculate the function's return value.
-
k is a constant computed by the first formula and used in the second formula
-
R is the Reynolds number that corresponds to the pipe with the larger diameter (
reynolds_number) -
D is the diameter of the larger pipe in meters (
larger_diameter) -
d is the diameter of the smaller pipe in meters (
smaller_diameter) -
P is the lost pressure kilopascals
-
ρ is the density of water (998.2 kilogram / meter3)
-
v is the velocity of the water flowing through the larger diameter pipe in meters / second (
fluid_velocity)
-
Helpful information.
-
The preparation content for this lesson explains how to use
pytest,assert, andapproxto automatically verify that functions are correct. It also contains an example test function and links to additional documentation aboutpytest. -
The
pytestapproxfunction accepts optional named arguments. One of those named arguments is abs. The abs named argument causes theapproxfunction to compare the actual and expected values up to a specified digit after the decimal point and to ignore the following digits. For example, the following two lines of code cause pytest to compare the actual number returned frompressure_loss_from_fittingsto −0.306 to only the third digit after the decimal point and to ignore all digits in the actual number after the 6.assert pressure_loss_from_fittings(1.75, 5) == approx(-0.306, abs=0.001)Notice in the previous example, that the value for abs is 0.001, which causes the approx function to ignore all digits after the third digit after the decimal point.
-
This video about test functions (20 minutes) shows a BYU-Idaho faculty member writing two test functions and using
pytestto run them.
Milestone
Begin fixing and testing the water_flow.py program which was created by another
person. For this milestone you will write test functions to test three of the functions in
water_flow.py. You will use the results of the tests to identify problems that you
will fix.
You will find errors in the provided code. Some functions work, some have errors, and some are not yet implemented. If a test fails it could be one of two reasons, either the function is not implemented correctly, or the test is not implemented correctly. You will have to figure out which one and fix where needed.
- Create a folder for this week's project, name it whatever you want.
- Download the water_flow.py program and save it in the folder you created.
- Open the folder you just created in VSCode.
- Create a file named
test_water_flow.pyin your project directory. - Add the following import statements at the top of your test_water_flow.py file.
from pytest import approx import pytest -
Copy and paste the following code at the bottom of your
test_water_flow.pyfile.# Call the main function that is part of pytest so that the # computer will execute the test functions in this file. pytest.main(["-v", "--tb=line", "-rN", __file__]) -
In your
test_water_flow.pyfile, write a test function namedtest_water_column_height. This test function must callwater_column_heightat least four times to verify that it is working correctly. Use the following numbers in your test function.Tower
HeightTank Wall
HeightExpected Water
Column Height0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 10.0 7.5 25.0 0.0 25.0 48.3 12.8 57.9 Tips:- Don't forget to import the function from
water_flow.py - Write one test at a time, test it then move on.
- Don't forget to import the function from
-
In your
test_water_flow.pyfile, write a test function namedtest_pressure_gain_from_water_height. This test function must callpressure_gain_from_water_heightat least three times to verify that it is working correctly. Use the following numbers in your test function.Height Expected
Pressureapprox
Absolute
Tolerance0.0 0.000 0.001 30.2 295.628 0.001 50.0 489.450 0.001 -
In your
test_water_flow.pyfile, write a test function namedtest_pressure_loss_from_pipe. This test function must callpressure_loss_from_pipeat least seven times to verify that it is working correctly. Use the following numbers in your test function.Pipe
DiameterPipe
LengthFriction
FactorFluid
VelocityExpected
Pressure
Lossapprox
Absolute
Tolerance0.048692 0.00 0.018 1.75 0.000 0.001 0.048692 200.00 0.000 1.75 0.000 0.001 0.048692 200.00 0.018 0.00 0.000 0.001 0.048692 200.00 0.018 1.75 -113.008 0.001 0.048692 200.00 0.018 1.65 -100.462 0.001 0.286870 1000.00 0.013 1.65 -61.576 0.001 0.286870 1800.75 0.013 1.65 -110.884 0.001 - Run your
test_water_flow.pyfile and ensure that all three of the test functions pass.
Milestone Submission
On or before the due date, return to Canvas and report your progress on this milestone.
Project Completion
Finish your project by completing the remaining test functions and correcting any errors discovered.
-
In your
test_water_flow.pyfile, write a test function namedtest_pressure_loss_from_fittings. This test function must callpressure_loss_from_fittingsat least five times to verify that it is working correctly. Use the following numbers in your test function.Fluid
VelocityQuantity
of FittingsExpected
Pressure
Lossapprox
Absolute
Tolerance0.00 3 0.000 0.001 1.65 0 0.000 0.001 1.65 2 -0.109 0.001 1.75 2 -0.122 0.001 1.75 5 -0.306 0.001 -
In your
test_water_flow.pyfile, write a test function namedtest_reynolds_number. This test function must callreynolds_numberat least five times to verify that it is working correctly. Use the following numbers in your test function.Hydraulic
DiameterFluid
VelocityExpected
Reynolds
Numberapprox
Absolute
Tolerance0.048692 0.00 0 1 0.048692 1.65 80069 1 0.048692 1.75 84922 1 0.286870 1.65 471729 1 0.286870 1.75 500318 1 -
In your
test_water_flow.pyfile, write a test function namedtest_pressure_loss_from_pipe_reduction. This test function must callpressure_loss_from_pipe_reductionat least three times to verify that it is working correctly. Use the following numbers in your test function.Larger
DiameterFluid
VelocityReynolds
NumberSmaller
DiameterExpected
Pressure
Lossapprox
Absolute
Tolerance0.28687 0.00 1 0.048692 0.000 0.001 0.28687 1.65 471729 0.048692 -163.744 0.001 0.28687 1.75 500318 0.048692 -184.182 0.001
Testing Procedure
Verify that your test program works correctly by following each step in this procedure:
-
Run your
test_water_flow.pyfile and ensure that all six of the test functions pass. If any of the test functions don’t pass, there is a mistake in either the program function that you wrote or the test function that you wrote. Read the output frompytest, fix the mistake, and run thetest_water_flow.pyfile again until all the test functions pass.> python test_water_flow.py ========================== test session starts ========================== platform win32 -- Python 3.11.1, pytest-7.2.1, pluggy-1.0.0 -- rootdir: C:\Users\cse111\week03 collected 3 items test_water_flow.py::test_water_column_height PASSED [ 16%] test_water_flow.py::test_pressure_gain_from_water_height PASSED [ 33%] test_water_flow.py::test_pressure_loss_from_pipe PASSED [ 50%] test_water_flow.py::test_pressure_loss_from_fittings PASSED [ 66%] test_water_flow.py::test_reynolds_number PASSED [ 83%] test_water_flow.py::test_pressure_loss_from_pipe_reduction PASSED [100%] =========================== 3 passed in 0.08s ===========================
-
Run your finished
water_flow.pyprogram. Enter the input shown below and ensure that your program prints the output shown below.Height of water tower (meters): 36.6 Height of water tank walls (meters): 9.1 Length of supply pipe from tank to lot (meters): 1524.0 Number of 90° angles in supply pipe: 3 Length of pipe from supply to house (meters): 15.2 Pressure at house: 158.7 kilopascals
Exceeding the Requirements
If your program fulfills the requirements for this assignment as described above, your program will earn 93% of the possible points. In order to earn the remaining 7% of points, you will need to add one or more features to your program so that it exceeds the requirements. Use your creativity to add features. Add a comment to the top of your code that explains your enhancement(s). Here are a few suggestions for additional features.
-
Inside the functions of your
water_flow.pyprogram, you may have typed numbers for Earth’s acceleration of gravity, the density of water, and the dynamic viscosity of water. Instead of using the numbers inside your functions, define the following constants outside your functions. Then use the constant names in place of the numbers inside your functions.Name Value EARTH_ACCELERATION_OF_GRAVITY 9.8066500 WATER_DENSITY 998.2000000 WATER_DYNAMIC_VISCOSITY 0.0010016 -
The functions that you wrote for this assignment, calculate water pressure in kilopascals (kPa). In the United States, water pressure is usually expressed in pounds per square inch (psi). Write a function in your
water_flow.pyprogram that converts kPa to psi. Then at the bottom of yourmainfunction, add code that calls your conversion function and prints the final pressure value in both kPa and psi. -
Add a test function to your
test_water_flow.pyfile that verifies that your psi-from-kPa conversion function works correctly. In your test function, call your conversion function multiple times so that your test function is a rigorous test.
If you choose to "exceed requirements" place a comment at the top of your code file that describes what you did to enhance your program.
Project Submission
Return to Canvas and upload your
water_flow.py and test_water_flow.py files for feedback.
If an error prevents your program from running to completion the grader will score your assignment with a 0 and request that you fix and resubmit your program. In other words, rather than submitting a program that doesn't work, it's best to ask for help to understand how to fix the problem before submitting your program.
Useful Links:
- Return to: Week Overview | Course Home
